High Temperature Ball Bearing Price And Quantity
- 10 Piece
High Temperature Ball Bearing Trade Information
- 100 Piece Per Week
- 1 Week
Product Description
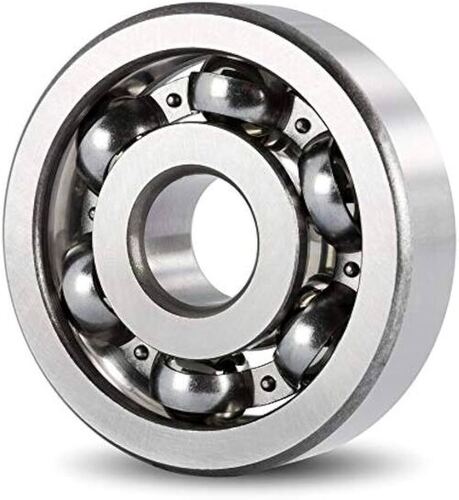
High Temperature Ball Bearing
High-temperature ball bearings are specially designed to withstand extreme heat, typically exceeding 250C (480F) and sometimes reaching up to 400C (750F). They are crucial components in various industries where machinery operates under intense thermal stress, such as
Steel mills and foundries
Bearings for conveyor belts
rolling mill stands
furnace equipment
Power generation
Bearings in turbines
steam generators and other high-temperature components.
Chemical processing :- Bearings in pumps, reactors, and other equipment handling hot chemicals.
Aerospace: Bearings in jet engines, rocket motors, and other high-performance applications.
Here's what sets high-temperature ball bearings apart from their standard counterparts:
Specialized materials: The rings, balls, and cages are made from heat-resistant materials like high-temperature steel, ceramic, or special alloys. These materials can maintain their dimensional stability and mechanical properties at elevated temperatures.
High-temperature lubricants: Standard grease lubricants would melt or degrade at high temperatures. High-temperature bearings use special lubricants like synthetic greases, fluorinated greases, or solid lubricants like molybdenum disulfide (MoS2).
Design features: They often have larger internal clearances to accommodate thermal expansion and prevent seizing. They may also have special sealing arrangements to keep out contaminants and retain lubricant.
Here are some of the key benefits of using high-temperature ball bearings:
Increased reliability and lifespan: They can operate in harsh environments without failing prematurely, reducing maintenance downtime and costs.
Improved efficiency: They can operate with lower friction at high temperatures, leading to reduced energy consumption.
Wider operating range: They enable the use of machinery in applications with extreme thermal conditions.
Here are some of the different types of high-temperature ball bearings available:
Deep groove ball bearings: The most common type, suitable for moderate temperatures and combined radial and axial loads.
Angular contact ball bearings: Can handle higher axial loads than deep groove bearings.
Ceramic ball bearings: Offer excellent heat resistance and wear resistance, but can be more expensive.
Solid-lubricated bearings: Use solid lubricants like MoS2 for operation in extreme temperatures or vacuum environments.
Other Products in 'High Temperature Bearing' category
 |
TECHNO OVERSEAS
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |







 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS